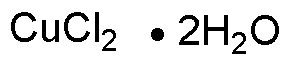Copper(II) chloride dihydrate is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Catalysis: It serves as an effective catalyst in various organic reactions, enhancing reaction rates and yields, particularly in the synthesis of fine chemicals.
- Analytical Chemistry: This compound is commonly used in analytical procedures, such as colorimetric assays for detecting the presence of certain ions, making it valuable for environmental testing.
- Electroplating: In the electroplating industry, it is employed to deposit copper onto surfaces, providing corrosion resistance and improving conductivity in electronic components.
- Wood Preservation: Its antifungal properties make it a key ingredient in wood treatment products, helping to protect against decay and insect damage in construction and furniture.
- Textile Industry: Copper(II) chloride dihydrate is used in dyeing processes, particularly for producing vibrant colors in fabrics, thus enhancing the aesthetic appeal of textiles.
General Information
Properties
Safety and Regulations
Applications
Copper(II) chloride dihydrate is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Catalysis: It serves as an effective catalyst in various organic reactions, enhancing reaction rates and yields, particularly in the synthesis of fine chemicals.
- Analytical Chemistry: This compound is commonly used in analytical procedures, such as colorimetric assays for detecting the presence of certain ions, making it valuable for environmental testing.
- Electroplating: In the electroplating industry, it is employed to deposit copper onto surfaces, providing corrosion resistance and improving conductivity in electronic components.
- Wood Preservation: Its antifungal properties make it a key ingredient in wood treatment products, helping to protect against decay and insect damage in construction and furniture.
- Textile Industry: Copper(II) chloride dihydrate is used in dyeing processes, particularly for producing vibrant colors in fabrics, thus enhancing the aesthetic appeal of textiles.
Documents
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
Product Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
DownloadProduct Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
DownloadCertificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.