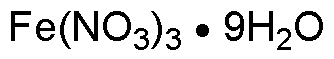Iron(III) nitrate nonahydrate is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Analytical Chemistry: It serves as a reagent in various analytical techniques, such as spectrophotometry, to determine the concentration of other compounds in a solution.
- Material Science: This compound is used in the synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles, which have applications in catalysis, magnetic materials, and drug delivery systems.
- Agriculture: It acts as a nitrogen source in fertilizers, promoting plant growth and enhancing soil fertility, particularly in iron-deficient soils.
- Textile Industry: Iron(III) nitrate nonahydrate is utilized in dyeing processes, helping to fix dyes onto fabrics and improve color fastness.
- Environmental Science: It is employed in the treatment of wastewater, aiding in the removal of contaminants through precipitation and coagulation processes.
General Information
Properties
Safety and Regulations
Applications
Iron(III) nitrate nonahydrate is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Analytical Chemistry: It serves as a reagent in various analytical techniques, such as spectrophotometry, to determine the concentration of other compounds in a solution.
- Material Science: This compound is used in the synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles, which have applications in catalysis, magnetic materials, and drug delivery systems.
- Agriculture: It acts as a nitrogen source in fertilizers, promoting plant growth and enhancing soil fertility, particularly in iron-deficient soils.
- Textile Industry: Iron(III) nitrate nonahydrate is utilized in dyeing processes, helping to fix dyes onto fabrics and improve color fastness.
- Environmental Science: It is employed in the treatment of wastewater, aiding in the removal of contaminants through precipitation and coagulation processes.
Documents
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
Product Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
DownloadProduct Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
DownloadCertificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.