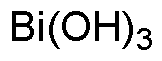Bismuth hydroxide is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Pharmaceuticals: It serves as an active ingredient in some antacid formulations, providing relief from gastrointestinal discomfort due to its ability to neutralize stomach acid.
- Cosmetics: Its antibacterial properties make it a valuable component in skincare products, particularly for treating acne and other skin irritations.
- Analytical Chemistry: Bismuth hydroxide is used in various analytical techniques, including as a reagent for detecting certain metal ions, enhancing the accuracy of chemical analyses.
- Environmental Applications: It can be employed in water treatment processes to remove heavy metals, contributing to cleaner water sources and reducing environmental pollution.
- Material Science: Bismuth hydroxide is explored as a potential component in the development of advanced materials, such as catalysts and semiconductors, due to its unique properties.
General Information
Properties
Safety and Regulations
Applications
Bismuth hydroxide is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Pharmaceuticals: It serves as an active ingredient in some antacid formulations, providing relief from gastrointestinal discomfort due to its ability to neutralize stomach acid.
- Cosmetics: Its antibacterial properties make it a valuable component in skincare products, particularly for treating acne and other skin irritations.
- Analytical Chemistry: Bismuth hydroxide is used in various analytical techniques, including as a reagent for detecting certain metal ions, enhancing the accuracy of chemical analyses.
- Environmental Applications: It can be employed in water treatment processes to remove heavy metals, contributing to cleaner water sources and reducing environmental pollution.
- Material Science: Bismuth hydroxide is explored as a potential component in the development of advanced materials, such as catalysts and semiconductors, due to its unique properties.
Documents
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
Product Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
DownloadProduct Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
DownloadCertificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.