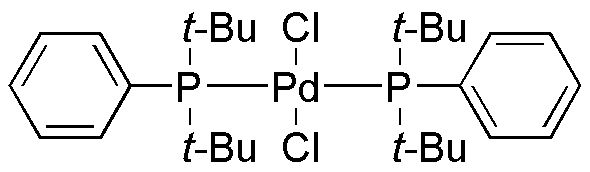Dichlorobis(di-tert-butylphenylphosphine)palladium(II) is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Catalysis: This compound serves as a highly effective catalyst in various organic reactions, including cross-coupling reactions such as Suzuki and Heck reactions, which are essential in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals.
- Material Science: It is used in the development of advanced materials, particularly in the creation of conductive polymers and nanomaterials, enhancing properties like electrical conductivity and mechanical strength.
- Pharmaceutical Development: Researchers leverage its catalytic properties to streamline the synthesis of complex drug molecules, improving efficiency and reducing the number of steps in the manufacturing process.
- Environmental Chemistry: The compound is applied in the degradation of pollutants through catalytic processes, contributing to environmental remediation efforts by breaking down hazardous substances.
- Research and Development: Its unique properties make it a valuable tool in academic and industrial laboratories for exploring new chemical reactions and developing innovative synthetic methodologies.
General Information
Properties
Safety and Regulations
Applications
Dichlorobis(di-tert-butylphenylphosphine)palladium(II) is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Catalysis: This compound serves as a highly effective catalyst in various organic reactions, including cross-coupling reactions such as Suzuki and Heck reactions, which are essential in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals.
- Material Science: It is used in the development of advanced materials, particularly in the creation of conductive polymers and nanomaterials, enhancing properties like electrical conductivity and mechanical strength.
- Pharmaceutical Development: Researchers leverage its catalytic properties to streamline the synthesis of complex drug molecules, improving efficiency and reducing the number of steps in the manufacturing process.
- Environmental Chemistry: The compound is applied in the degradation of pollutants through catalytic processes, contributing to environmental remediation efforts by breaking down hazardous substances.
- Research and Development: Its unique properties make it a valuable tool in academic and industrial laboratories for exploring new chemical reactions and developing innovative synthetic methodologies.
Documents
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
Product Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
DownloadProduct Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
DownloadCertificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.