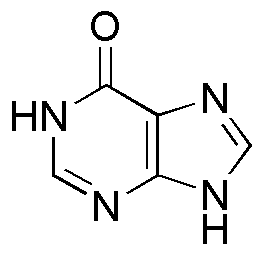
Hypoxanthine is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Biochemical Research: It serves as a key substrate in the study of purine metabolism, helping researchers understand cellular energy processes and nucleotide synthesis.
- Pharmaceutical Development: Hypoxanthine is used in the formulation of drugs aimed at treating conditions like gout and certain types of cancer, providing a basis for developing effective therapies.
- Cell Culture Media: This compound is often included in cell culture media to support the growth of various cell types, enhancing the viability and proliferation of cells in laboratory settings.
- Genetic Studies: It plays a role in the study of genetic mutations and repair mechanisms, aiding researchers in understanding diseases at the molecular level.
- Food Industry: Hypoxanthine is utilized as a flavor enhancer in certain food products, contributing to the umami taste and improving overall flavor profiles.
General Information
Properties
Safety and Regulations
Applications
Hypoxanthine is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Biochemical Research: It serves as a key substrate in the study of purine metabolism, helping researchers understand cellular energy processes and nucleotide synthesis.
- Pharmaceutical Development: Hypoxanthine is used in the formulation of drugs aimed at treating conditions like gout and certain types of cancer, providing a basis for developing effective therapies.
- Cell Culture Media: This compound is often included in cell culture media to support the growth of various cell types, enhancing the viability and proliferation of cells in laboratory settings.
- Genetic Studies: It plays a role in the study of genetic mutations and repair mechanisms, aiding researchers in understanding diseases at the molecular level.
- Food Industry: Hypoxanthine is utilized as a flavor enhancer in certain food products, contributing to the umami taste and improving overall flavor profiles.
Documents
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
Product Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
*Catalog Number
*Lot Number
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.
*Catalog Number
*Lot Number
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
DownloadProduct Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
DownloadCertificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
*Catalog Number
*Lot Number
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.