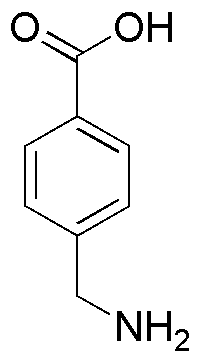
(4-Aminomethyl) benzoic acid is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Pharmaceutical Development: This compound serves as a key intermediate in the synthesis of various pharmaceuticals, particularly in the development of analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Polymer Chemistry: It is used in the production of specialty polymers, enhancing material properties such as thermal stability and mechanical strength, making it valuable in the plastics industry.
- Biochemical Research: Researchers employ this compound in biochemical assays and studies related to enzyme activity, providing insights into metabolic pathways.
- Cosmetic Formulations: Its properties make it suitable for use in cosmetic products, where it acts as a pH adjuster and stabilizer, improving product efficacy and shelf life.
- Agricultural Chemicals: The compound is also explored in the formulation of agrochemicals, where it can enhance the effectiveness of herbicides and pesticides, contributing to improved crop yields.
General Information
Properties
Safety and Regulations
Applications
(4-Aminomethyl) benzoic acid is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Pharmaceutical Development: This compound serves as a key intermediate in the synthesis of various pharmaceuticals, particularly in the development of analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Polymer Chemistry: It is used in the production of specialty polymers, enhancing material properties such as thermal stability and mechanical strength, making it valuable in the plastics industry.
- Biochemical Research: Researchers employ this compound in biochemical assays and studies related to enzyme activity, providing insights into metabolic pathways.
- Cosmetic Formulations: Its properties make it suitable for use in cosmetic products, where it acts as a pH adjuster and stabilizer, improving product efficacy and shelf life.
- Agricultural Chemicals: The compound is also explored in the formulation of agrochemicals, where it can enhance the effectiveness of herbicides and pesticides, contributing to improved crop yields.
Documents
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
Product Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
*Catalog Number
*Lot Number
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.
*Catalog Number
*Lot Number
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
DownloadProduct Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
DownloadCertificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
*Catalog Number
*Lot Number
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.