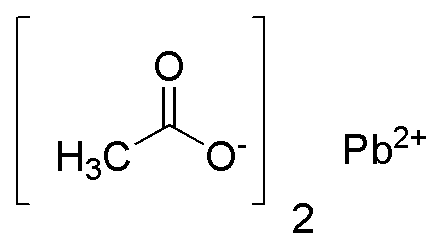
Lead(II) acetate basic, anhydrous is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Analytical Chemistry: It serves as a reagent in various analytical procedures, particularly in the detection of sulfide ions in solution, providing a reliable method for environmental monitoring.
- Organic Synthesis: This compound is used in organic chemistry for the synthesis of other lead compounds, which can be essential in developing new materials or pharmaceuticals.
- Textile Industry: It acts as a mordant in dyeing processes, enhancing color retention on fabrics, which is crucial for producing vibrant textiles.
- Glass Manufacturing: Lead(II) acetate is employed in the production of lead glass, known for its clarity and brilliance, making it a preferred choice in high-quality glassware.
- Research and Development: It is used in laboratories for various experimental applications, including studies on lead's biological effects, aiding in understanding its impact on health and the environment.
General Information
Properties
Safety and Regulations
Applications
Lead(II) acetate basic, anhydrous is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Analytical Chemistry: It serves as a reagent in various analytical procedures, particularly in the detection of sulfide ions in solution, providing a reliable method for environmental monitoring.
- Organic Synthesis: This compound is used in organic chemistry for the synthesis of other lead compounds, which can be essential in developing new materials or pharmaceuticals.
- Textile Industry: It acts as a mordant in dyeing processes, enhancing color retention on fabrics, which is crucial for producing vibrant textiles.
- Glass Manufacturing: Lead(II) acetate is employed in the production of lead glass, known for its clarity and brilliance, making it a preferred choice in high-quality glassware.
- Research and Development: It is used in laboratories for various experimental applications, including studies on lead's biological effects, aiding in understanding its impact on health and the environment.
Documents
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
Product Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
*Catalog Number
*Lot Number
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.
*Catalog Number
*Lot Number
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
DownloadProduct Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
DownloadCertificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
*Catalog Number
*Lot Number
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.