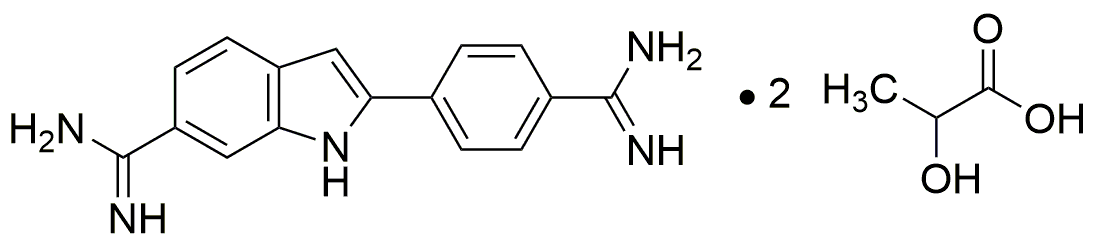
DAPI, dilactate is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Cell Staining: Commonly used in fluorescence microscopy to stain DNA in cells, allowing researchers to visualize cell nuclei and assess cell health.
- Apoptosis Studies: Helps in identifying apoptotic cells by differentiating between live and dead cells, providing insights into cell death mechanisms.
- Neuroscience Research: Used to label neuronal cells, facilitating the study of neural networks and brain structure in various neurological studies.
- Drug Development: Assists in evaluating the effects of new pharmaceuticals on cell viability and proliferation, crucial for developing effective treatments.
- Environmental Monitoring: Employed in assessing the impact of pollutants on cellular systems, aiding in environmental health research.
General Information
Properties
Safety and Regulations
Applications
DAPI, dilactate is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Cell Staining: Commonly used in fluorescence microscopy to stain DNA in cells, allowing researchers to visualize cell nuclei and assess cell health.
- Apoptosis Studies: Helps in identifying apoptotic cells by differentiating between live and dead cells, providing insights into cell death mechanisms.
- Neuroscience Research: Used to label neuronal cells, facilitating the study of neural networks and brain structure in various neurological studies.
- Drug Development: Assists in evaluating the effects of new pharmaceuticals on cell viability and proliferation, crucial for developing effective treatments.
- Environmental Monitoring: Employed in assessing the impact of pollutants on cellular systems, aiding in environmental health research.
Documents
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
Product Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
*Catalog Number
*Lot Number
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.
*Catalog Number
*Lot Number
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
DownloadProduct Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
DownloadCertificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
*Catalog Number
*Lot Number
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.