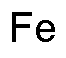Iron is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Construction and Infrastructure: Iron is a primary material in the construction industry, used for beams, reinforcements, and structural components due to its strength and durability.
- Manufacturing of Steel: As a key ingredient in steel production, iron enhances the hardness and tensile strength of steel, making it essential for automotive, aerospace, and machinery industries.
- Magnetic Applications: Iron's magnetic properties are exploited in various applications, including transformers, electric motors, and magnetic storage devices, providing efficient energy conversion and storage.
- Biomedical Uses: Iron compounds are crucial in medicine, particularly in the formulation of supplements and treatments for iron deficiency anemia, improving patient health and energy levels.
- Catalysis: In chemical processes, iron acts as a catalyst in various reactions, such as the Haber process for ammonia synthesis, enhancing efficiency and reducing energy consumption.
General Information
Properties
Safety and Regulations
Applications
Iron is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Construction and Infrastructure: Iron is a primary material in the construction industry, used for beams, reinforcements, and structural components due to its strength and durability.
- Manufacturing of Steel: As a key ingredient in steel production, iron enhances the hardness and tensile strength of steel, making it essential for automotive, aerospace, and machinery industries.
- Magnetic Applications: Iron's magnetic properties are exploited in various applications, including transformers, electric motors, and magnetic storage devices, providing efficient energy conversion and storage.
- Biomedical Uses: Iron compounds are crucial in medicine, particularly in the formulation of supplements and treatments for iron deficiency anemia, improving patient health and energy levels.
- Catalysis: In chemical processes, iron acts as a catalyst in various reactions, such as the Haber process for ammonia synthesis, enhancing efficiency and reducing energy consumption.
Documents
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
Product Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
*Catalog Number
*Lot Number
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.
*Catalog Number
*Lot Number
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
DownloadProduct Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
DownloadCertificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
*Catalog Number
*Lot Number
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.